By: Allison Benson, Physical Therapy student at Hunter College, graduating in May 2018
Worked with Kristin Romeo, PT, DPT
With injury and with age, the joints of your body can be damaged by osteoarthritis, causing painful, aching joints. This pain can follow you throughout the day. You may feel stiff waking up, feel a dull ache when taking your dog for a walk, or feel a painful grinding as you stand up from sitting or as you climb the stairs.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disorder in the United States and is more common in women than men, according to an article published by Zhang & Jordan (2010). In healthy joints, where two or more bones meet and rub together, the bone surfaces are covered by a slippery substance called hyaline cartilage. This cartilage helps make your joints move smoothly and painlessly. With OA, this cartilage has broken down, leaving the bones exposed to each other, creating a grating or “bone on bone” feeling.

When a joint with OA becomes very painful, surgeons often recommend a total joint replacement—you probably know someone who has had a total knee or total hip replacement due to OA. Hips and knees are common sites for OA to develop, both because they move a lot, and because they carry the weight of the body.
You may not have heard of a total ankle replacement, though. Although ankles are also weight-bearing and mobile, they develop OA much less common; only about 1% of the population develops ankle OA (Valderrabano et al., 2009). This means many fewer people have ankle surgeries related to OA.
Another reason you may not have heard about ankle replacement is that it was a relatively unpopular surgery until recently. Total ankle replacements are complicated because there are a lot of important structures packed into a small area at the ankle. They also were associated with a very high failure rate, with surgeons needing to go back in and complete additional surgeries to replace, remove, or adjust the hardware they had placed.
That said, the popularity and success rate of total ankle replacements are on the rise.
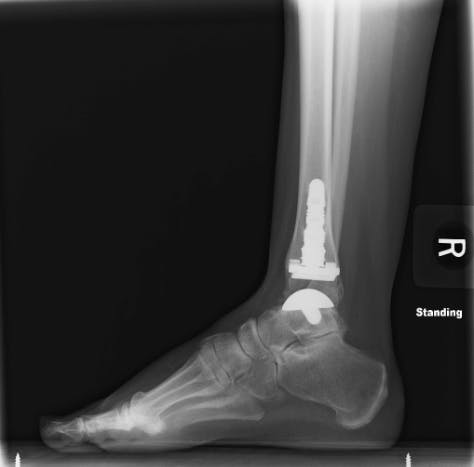
In this surgery, a round metal ball is implanted into the talus, which is an important bone in your ankle. A metal implant is also implanted into the bottom of your tibia, which is the big bone in your calf. A plastic spacer is placed between these two pieces, which allows the tibia to slide smoothly on the talus, just like it does in healthy ankles.
After surgery, a patient will typically be in a surgical boot for 8-10 weeks, and cannot put weight on that foot for 4-6 weeks (Devries, Scharer, & Sigl, 2015). Patients may be referred to physical therapy prior to, or immediately following the procedure for prehab or rehab of the ankle.
Immediately after the surgery, therapists help with gentle work to reduce swelling and pain and prevent tissues from binding down as scar tissue forms. As time passes, therapists help patients regain their strength and range of motion, restoring their ankle to full use. Healing from an ankle surgery is a long process, and requires months of physical therapy, but can be a good option when faced with debilitating ankle OA.
Did you recently have a Total Ankle Replacement surgery? We can help. Schedule your appointment today.
Fill out my online form.
SOURCES
Devries, Scharer, & Sigl. (2015). Total Ankle Arthroplasty Rehab Protocol. BayCare Clinic; Foot & Ankle Center.
Zhang, Y., & Jordan, J. M. (2010). Epidemiology of Osteoarthritis. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine, 26(3), 355–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2010.03.001. Retrieved from
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2920533/
Valderrabano, V., Horisberger, M., Russell, I., Dougall, H., & Hintermann, B. (2009). Etiology of Ankle Osteoarthritis. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 467(7), 1800–1806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0543-6
.png?auto=format&auto=compress&h=150)