In October of 2017, NFL star defensive end JJ Watt of the Houston Texans crashed into an opposing quarterback while attempting a tackle. He was carted off the field on a stretcher with a tibial plateau fracture (TPF).
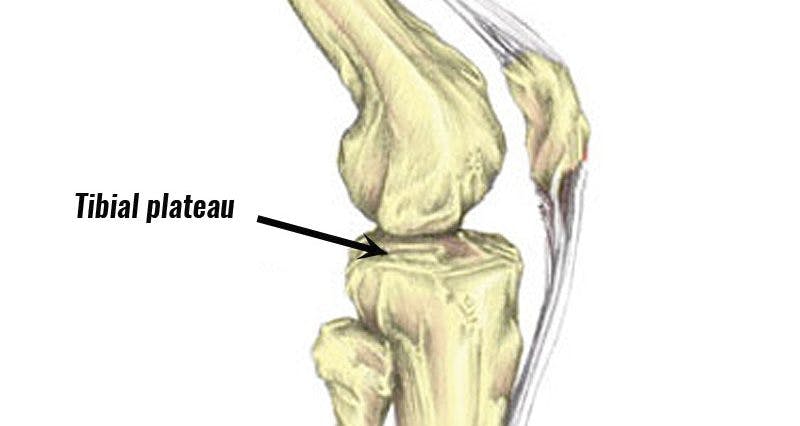
Watt had suffered a break in a part of his shin bone (tibia), called the tibia plateau. It’s a serious injury of a bone structure that is most involved in supporting the knee and body weight generally.
On this page we look closely at recovery from this injury, specifically:
- What is a Tibial Plateau Fracture?
- Who Most Is Most Often Afflicted By It?
- How Long is Tibial Plateau Fracture Recovery Time?
- How is it treated?
What is a Tibial Plateau Fracture?
Tibial plateau fractures are without doubt a high-damage injury, and need intensive rehab. The tibia is a key bone structure that supports your body weight as you run, walk or jump, the tibia plateau being its upper portion. A fracture of the plateau is caused by a high-energy impact, the kind of injury that can also affect ligaments of the knee, soft tissue and cause other collateral structures.
Suffering a tibial plateau fracture causes pain, swelling, and decreased ability to move the knee.
All that said, JJ Watt returned to the gridiron after a year and is playing again today. And while few of us have the body strength of an elite athlete, you can be optimistic about recovery, working with expert therapists at Park Sports.
Who Is Most Often Afflicted By a TPF?
At Park Sports we work most often on TPF with people over age 50, who have suffered from falls or other accidents. But younger people may suffer TPF while skiing, or in motocross, car accidents, and other situations.
With people aged 50 and over, treatment will have as its goal the return to ordinary daily activities, rather than a return to sport. However, if this injury is sports-related, our team of former and current athlete therapists can assist your needs as well.
How Long is Tibial Plateau Fracture Recovery Time?
The length of recovery depends largely on whether surgery has been performed. Luckily, in many cases, surgery is not required, but if there is displacement (if the bone has moved) then surgery may be necessary.
Non-displaced tibial plateau fractures take up to 3-4 months without surgery to heal. When surgery is required these cases take around 4 months to heal. After this healing period, Physical Therapy most often continues until at 6 months, a patient is typically able to return to a normal life, albeit with certain limitations.
That is a real milestone, compared to a patient’s first six weeks which are most often on crutches or in a brace. Note that 100% complete recovery, while varied, can take a year or more, and athletes will need sports/specific bodywork during that year. (See below)
Physical Therapy for Tibial Plateau Fracture: How is it Treated?
Over time, your therapist will focus generally on restoring full joint range of motion and activating the leg muscles. But each individual is different, and a custom treatment plan must be developed.
That is why when composing your tibial plateau fracture recovery plan, we confer with you, your doctors and your surgical team to ensure that the plan is uniquely tailored to your needs. Some of what we might incorporate could include manual therapy, kinesiology taping, state-of-the-art strength and conditioning equipment, yoga therapy, and even neuromuscular rehabilitation.
Despite the variations in treating each individual, we can present a general look, based on the clinical data, at what treatment might be expected for a tibial plateau fracture. Again, this is a general timeline. Please keep in mind that it will almost certainly be altered to fit your needs.
Tibial Plateau Fracture Rehab: Weeks 1-6:
Your therapist will begin immediately with steps to reduce inflammation, calm pain, and begin to promote healing.
The therapist focuses on maintaining knee extension and non-weight-bearing movement to promote healing and to prevent further pain and reinjury. Exercises might include active and passive range of motion knee movements, lower body stretches, core strengthening exercises, and upper-body cardiovascular exercises on our state-of-the-art ergometer.
Tibial Plateau Fracture Rehab: Weeks 6-12:
The goals at this point are to work with the patient out of the brace to normalize gait, start work to regain full range-of-motion in the knee, and to begin to strengthen the lower body.
Exercises might include aggressive gait training (progressively putting more weight on the injured leg) and lower body strengthing exercises like squats, calve raises, bridges, and leg raises. At this point, cardiovascular exercise will begin to incorporate forms that include the lower body, like the stationary bike and our advanced AlterG treadmill.
Tibial Plateau Fracture Rehab: Week 12 – 6 Months:
The goal at this point in therapy is to gain full range of motion in knee flexion and extension, to have regained at least 80% of your leg strength, and to fully normalize your gait without any assistive device. Single-leg lower body strength exercises (e.g. split squats, lunges, and single-legged Romanian deadlifts), and other balancing exercises will begin to be incorporated.
Tibial Plateau Fracture Rehab: 6-12 months
After six months, non-athletes can return to their ordinary activities. Athletes will, by contrast, begin to implement sports-specific drills, plyometrics, unilateral exercises, and running on the AlterG treadmill for cardiovascular recuperation. A full return to sport may take up to 12 months.
As always, the speed and effectiveness of your recovery depends on the partnership of therapist and patient. If you wholeheartedly commit and finish your course of exercise, you are much more likely to recover faster and in a better and more complete way.
Our commitment to you is to provide dedicated guidance and expertise during every step of your recovery. Together, we can do this.
.png?auto=format&auto=compress&h=150)